TCFD stands for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures. The TCFD recommends that companies grasp and disclose information on what kinds of impacts (risks and opportunities) climate change will have on their financial performance and condition.
*With the disbandment of the TCFD in October 2023, supervision of the progress of companies’ information disclosures has been transferred from the TCFD to the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB). However, the TCFD recommendations remain valid.
TechMatrix recognizes that preserving and conserving the global environment is the foundation of the sustainable development and growth of the Group’s management. Based on this awareness, we have positioned measures to address climate change as one of our important management issues. For this reason, we are analyzing the impacts of climate change on the Group’s business in line with the TCFD recommendations, identifying risks and opportunities, and implementing response measures. Concurrently, we are disclosing relevant information based on the following framework:
Initiatives to Address Climate Change
Information Disclosure Based on the TCFD Recommendations
Governance
Board of Directors’ Oversight System for Response to Climate Change
The Sustainability Committee, which reports to the Executive Committee, the body responsible for overall business execution, manages progress on the response to climate change. The Sustainability Committee works closely with the Corporate Planning Dept., which is in charge of environmental management, to supervise the climate change response measures and related planning at each division, headquarters, department, branch and sales office. The Sustainability Committee comprises appointed members of departments within the Corporate Headquarters.
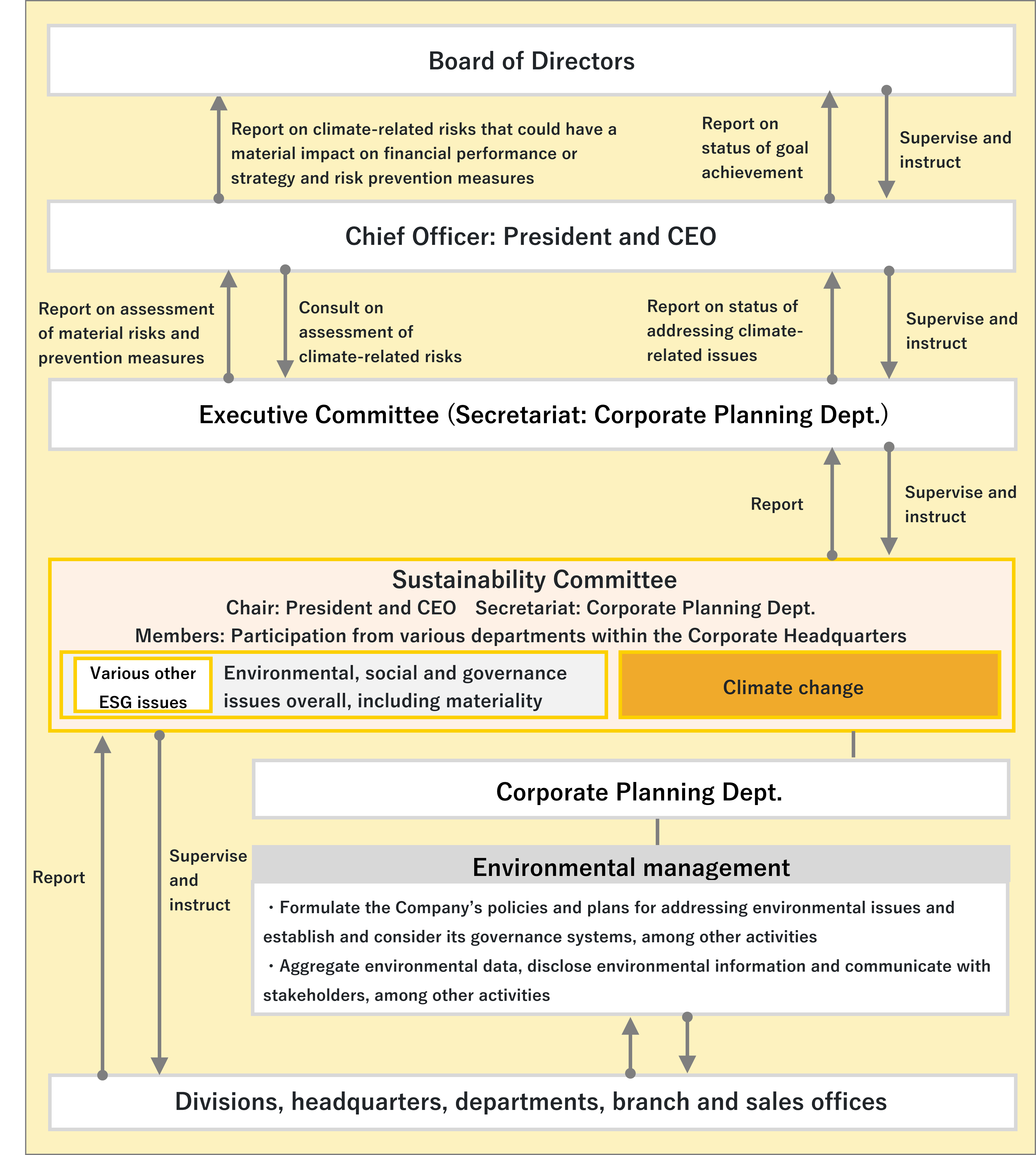
Roles of Top Management
TechMatrix has appointed the President and CEO as the Officer responsible for climate-related problems in the Board of Directors. The President and CEO also serves as the Chair of the Sustainability Committee.The President and CEO bears ultimate responsibility for assessing and managing climate-related risks and opportunities, developing strategies, and implementing specific measures.
Strategy
Basic policy on climate change
Climate change is a global issue that will cause significant changes to the global environment, which is the foundation for corporate business activities.
TechMatrix believes that fulfilling a company’s roles and responsibilities regarding climate change is an important management issue. Based on this belief, we have developed management strategies to implement our Medium-Term Management Plan “Creating Customer Value in the New Era”* as well as plans for climate change responses that are linked to specific business activities. Concurrently, we are advancing various measures to address the expected risks and opportunities.
Time Horizons for Climate Change-Related Risks and Opportunities (Short Term, Medium Term and Long Term)
Impacts of Climate-related Risks and Opportunities on the Organization’s Businesses, Strategy, and Financial Planning
Identification Process for Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities
* Please see “Identification and Assessment Processes for Climate-Related Risks” under “Risk Management.”Techmatrix Group’s Climate Strategy (Summary)
We have identified the risks and opportunities related to climate change and prepared climate strategies and action plans for risks and opportunities that have a particularly critical impact on our business. We have also conducted scenario analyses of those risks and opportunities whose impacts are thought to be relatively large, using the 1.5℃ and 4℃ scenarios and other parameters.
| Category | Risk/opportunity | Time horizon | Impact (response scenario) |
Group-wide strategy | Business strategy Information Infrastructure |
Business strategy Applications Services, Medical System |
| Physical risks (acute) | (1) Hindrance of procurement by natural disasters, etc. | Short to Long | Estimate loss of net sales expected in the event of delays in supply of our hardware due to impact of floods caused by climate change | Review BCP | ― |
― |
| Same as above | (2) Losses in the event of major system failure at a data center due to abnormal weather | Short to Long | No scenario analysis performed, due to low probability of occurrence, even though the impact would be major if it were to occur | Formulate BCPs for data centers | ― |
― |
| Transition risks (Technology) |
(3) Loss of growth opportunities and reduced net sales due to delays in responding to demand for decarbonization products and services | Medium to Long | No scenario analysis performed, due to assessment that financial impact would be small | •Participate in climate change-related initiatives •Promote green procurement •Products and services that contribute to reduction of GHG emissions |
•Promote green procurement •Products and services that contribute to reduction of GHG emissions |
― |
| Transition risks (Policy) |
(4) Increase in procurement costs due to climate change-related initiatives | Long | No scenario analysis performed, due to assessment that financial impact would be small | •Participate in climate change-related initiatives •Promote green procurement •Promote energy-saving activities and achieve 100% use of renewable energy |
•Promote green procurement | ― |
| Transition risks (Reputation) |
(5) Reputational damage to the Company as an organization due to delays in responding to decarbonization | Short to Medium | No scenario analysis performed, due to assessment that financial impact would be small | •Participate in climate change-related initiatives •Promote environmental initiatives •Disclose information on the website, CDP, etc. |
― |
― |
| Opportunities (products/services) |
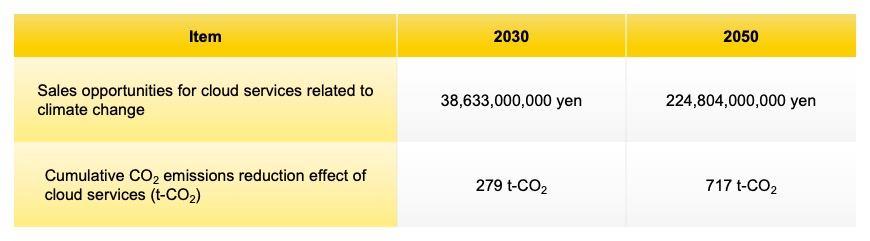
(6) Reduction of GHG emissions and response to risks through the use of services provided by the Group | Long | •Estimate increase in net sales from impact of climate change •Estimate CO2 emission curbing effect of transition to the Group’s cloud services |
•Visualize volume of GHG emissions reductions from the Group’s products and services •Achieve 100% use of renewable energy |
― |
•Visualize volume of GHG emissions reductions from the Group’s products and services •Address climate change risks by utilizing fintech |
| Other | GHG reduction measures by the Company | Short to Long | ― |
•Reduce energy used in business activities •Initiatives for GHG reductions across entire supply chain |
― |
― |
Techmatrix Group’s Climate Strategy (Details)
Climate change risks / impact (response scenarios) / countermeasures
(1) Procurement hindered by natural disasters, etc.
Details of risk
Purchasing of core products will be hindered by factors such as natural disasters caused by climate change
Purchasing from overseas manufacturers, including Palo Alto Networks, Inc. (U.S.A.) accounts for around 60% of the Group’s procurement amount. For this reason, if manufacturing is halted or transportation networks are disrupted due to factors such as natural disasters caused by climate change, purchasing of these core products may be hindered. (There is a similar risk associated with manufacturers in Japan.)
Scenario Analysis
In light of the possibility of delays in supply of products carried by the Group due to the impact of floods or other events caused by climate change, we estimated the amount of loss of net sales based on the IPCC AR6 and on the probability of floods occurring at our suppliers and customers.
Group-wide strategy
(2) Losses in the event of major system failure at a data center due to abnormal weather
Details of risk
Compensation for losses will be incurred if a major system failure occurs at a data center due to abnormal weather
The systems and cloud services provided by the Group play critical roles in our customers’ operations. If a major disruption occurs at a data center due to abnormal weather caused by climate change, the Group may be subject to compensation claims for losses.
Group-wide strategy
Formulate BCP for data centers
Many of the systems and cloud services provided by the Group use data centers that are located in highly flood-resistant areas. While it is difficult for the Group to exert influence, we strive to maintain the stable provision of services, including by obtaining cooperation across the entire supply chain to conduct regular checks of disaster countermeasures. In addition, some of our services use data centers that are managed by the Group. The Company has established systems and BCPs capable of responding to a variety of threats throughout the entire Group, and we will also establish and regularly review BCPs that take impact on data centers into consideration, in light of factors such as the future status of natural disaster occurrence due to climate change-related causes.
Further, once a year, the Group conducts operational drills in readiness for disasters, etc. and has built systems that will enable us to recover swiftly.
(3) Decrease in the competitiveness, loss of growth opportunities, and reduced net sales due to delays in responding to demand for decarbonization products and services
Details of risk
Technological development and collaboration and initiatives with suppliers for the decarbonization (high energy efficiency) of our own products will lag behind the increase in demand for carbon-free products and services, leading to a decline in competitiveness, loss of growth opportunities, and reduced net sales
Customers aiming for carbon neutrality (in Scope 3) may call for carbon-free (low-carbon) products and services. If this happens, collaboration across the entire supply chain, including the manufacturers that are the Group’s suppliers, will be essential, which will require a reasonable lead time. If customers’ needs increase rapidly and the Group’s initiatives in response lag behind, it could lead to a loss of growth opportunities and reduced net sales.
Group-wide strategy
Participate in climate change-related initiatives
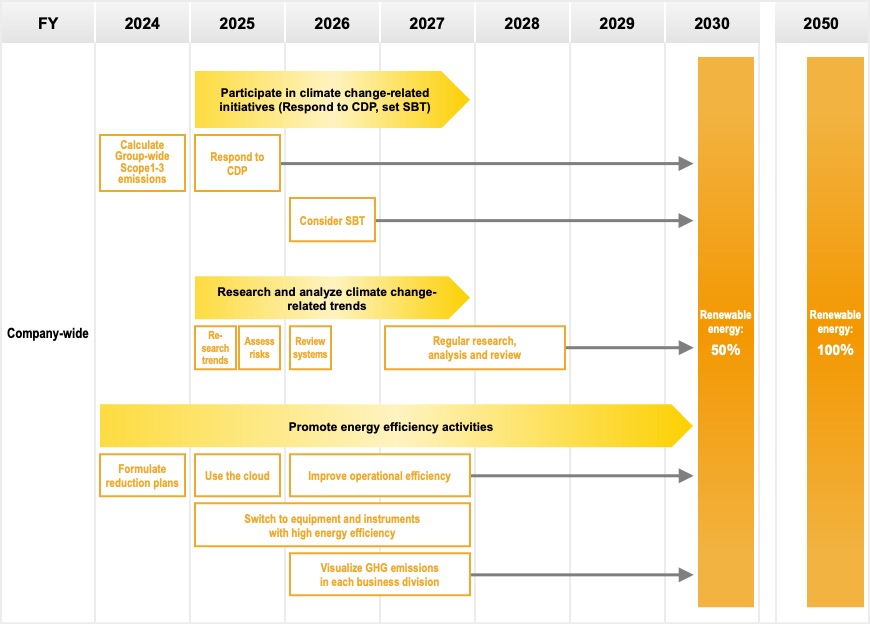
The Group has set a target of reducing GHG emissions by 46% by FY2030 (relative to the FY2020 level) and reaching net zero (covering Scope 1 and Scope 2) for all GHG emissions from business activities by 2050. We will strive to grasp an overall picture of emissions not only by the Company itself but by the Group’s supply chain and to set targets for their reduction. Further, we will participate in climate change-related initiatives such as SBT and CDP and cooperate with suppliers on global climate change countermeasures.
Information Infrastructure Business strategy
Promote green procurement
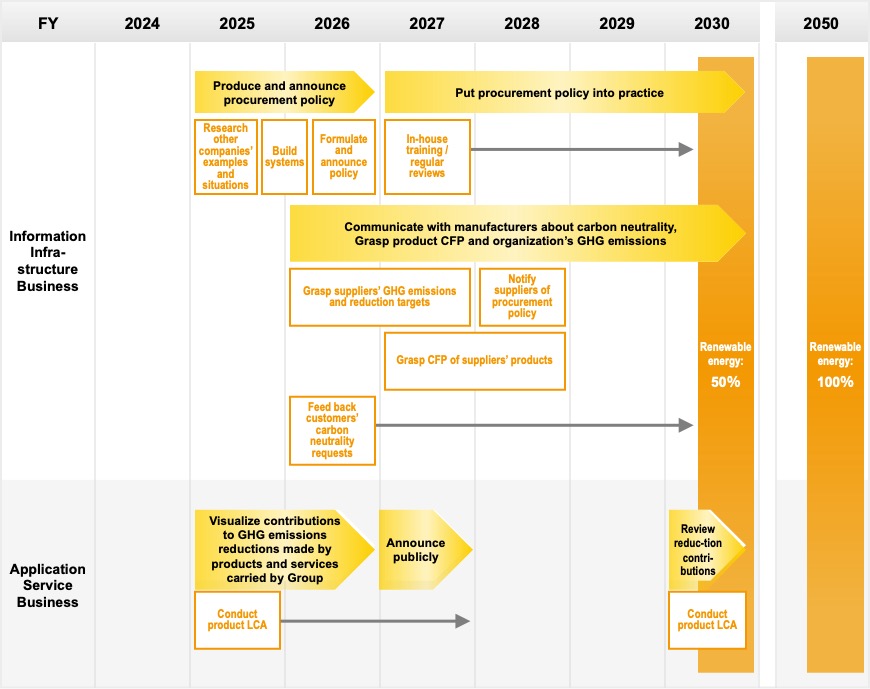
In the Information Infrastructure Business, we will formulate and publicly announce procurement policies concerning climate change. We will regularly review these procurement policies and, in addition to efforts to reduce the Business’s environmental footprint and increase added value with the entire life cycles of products in mind, we will strive to gain business opportunities and avoid risks. We believe that actively choosing products that have a small environmental footprint will make the Group less susceptible to carbon pricing and other impacts.
(4) Increase in procurement costs due to climate change-related initiatives
Details of risk
Increase in procurement costs due to global climate change-related initiatives
If customers aiming for carbon neutrality (in Scope 3) call for the provision of carbon-free (low-carbon) services, the costs of procurement of products could increase due to policies, laws and regulations, including renewable energy and carbon pricing.
Group-wide strategy
Promote energy-saving activities and achieve 100% use of renewable energy
The Company has set a target of increasing its rate of use of renewable energy at its business sites (Head Office, branch, and sales offices) to 50% by FY2030 and to 100% by 2050, and it is proceeding with the transition to carbon-free energy. In addition, the Company is engaged in energy efficiency activities at its business sites, including replacing equipment and instruments to those with higher energy efficiency and curbing energy consumption through operational efficiency improvements.
Information Infrastructure Business strategy
*Please refer to the Information Infrastructure Business strategy in (3) above for the following.
Promote green procurement
(5) Reputational damage to the Company as an organization due to delays in responding to decarbonization
Details of risk
Reputational damage to the Company as an organization due to delays in responding to decarbonization
Group-wide strategy
Promote environmental initiatives
Climate change opportunities/impacts (response scenarios)/responses
(6) Reduction of GHG emissions and response to risks through the use of services provided by the Group
Details of opportunity
Realize energy consumption reductions by customers and minimize their GHG emissions through their transition to cloud services provided by the Company
Power consumption in the IT sector continues to rise, and the reduction of GHGs from power consumption, as well as curbing of costs, has become a key challenge. The cloud services provided by the Company in various sectors are able to keep GHGs to a minimum, and we believe that the future increase in demand for DX and the realization of carbon neutrality will become a beneficial business opportunity for the Group.
Scenario analysis
Envisaging progress in the transition away from on-premise systems to the Group’s cloud services with customers’ growing needs for climate change countermeasures (CO2 reductions) and operational efficiency improvements, we estimated the increase in sales due to the impact of climate change.
We also envisaged the future CO2 emissions coefficient of grid power in Japan, based on the Energy Basic Plan, and estimated the CO2 emissions reduction effect of the transition to the Group’s cloud services.
Potential CO2 emissions reduction effect of cloud services provided by the Company
*The CO2 emission reduction effect described above is calculated based on values evaluated for each element individually.
Group-wide strategy
Visualize volume of GHG emissions reductions from the Group’s products and services
Because the Group’s products and services will remove the need for customers to own and manage server equipment and facilities, they can expect reductions in their power consumption. The spread of the Group’s cloud services that contribute to the reduction of GHG emissions will contribute to the reduction of GHG emissions across society as a whole. The Group will make the amount of these products’ contributions to our customers’ GHG emissions reductions transparent through such means as regularly requesting and grasping information disclosures about our suppliers’ carbon neutrality initiatives and contributions, and work to increase our business opportunities through these efforts.
Application Service Business, Medical System Business strategy
Visualize volume of GHG emissions reductions from the Group’s products and services
The products and services of the Application Service Business and Medical System Business improve the quality and productivity of customers’ business activities and are able to contribute to the reduction of man-hours. Specifically, products and services such as CRM systems for contact center operations, quality control systems for software development, BI tools, teaching support systems for educational institutions, and cloud systems for medical institutions and remote diagnosis support services are able to reduce customers’ man-hours (in other words, power consumption) and use of resources such as paper, enabling them to minimize GHG emissions as a result. In addition, reductions in power consumption can be expected as customers will no longer need to own and manage server equipment and facilities.
We will make the amount of these products’ and services’ contributions to our customers’ GHG emissions transparent and make efforts to expand business opportunities.
Future activity plans
Risk Management
Identification and Assessment Processes for Climate-Related Risks
The Group conducts identification and assessment of climate-related risks that have a crucial impact on financial performance and strategy under the leadership of the Internal Control Office, which leads the Company’s risk management, and the Corporate Planning Dept., which conducts environmental data aggregation, planning, and external disclosure. Following approval by the Group’s Chief Officer (President and CEO), this risk information is shared with various departments and companies.Specifically, risks are broadly classified as transition risks (policy and legal, technology, market, reputation), which require adaptation to climate change, and physical risks (acute, chronic), which require responses to the physical effects of climate change. For these items, the Group considers identification, assessment and related tasks using the same methodology as the processes described above.
Furthermore, during the risk identification and assessment process, risks determined to have a material impact based on the Company’s unique risk management methodology are identified as material risks.
Risk Management Process
At the Company, the Chief Officer consults with the Executive Committee (consisting of Executive Officers and Division Managers) on the assessment of climate risks, and the Executive Committee reports its assessment of material risks and risk prevention measures. The Corporate Planning Dept., which serves as the Executive Committee’s secretariat, works with the Internal Control Office to identify and assess climate-related risks in collaboration with each division, headquarters, department, branch and sales office, and places those matters before the Executive Committee. The Executive Committee discusses the climate-related risks placed before it, and material risks are assessed and monitored.The Chief Officer reports on climate-related risks that could have a material impact on financial performance or strategy and risk prevention measures, as important issues that should be placed on the Board of Directors’ agenda.
The Executive Committee shares the identified risks with various departments and companies, and each department and company considers specific individual response measures. The Executive Committee collects and monitors data on progress with these specific measures and, after verification (at least once a year), reflects progress in risk management activities for the following fiscal year.
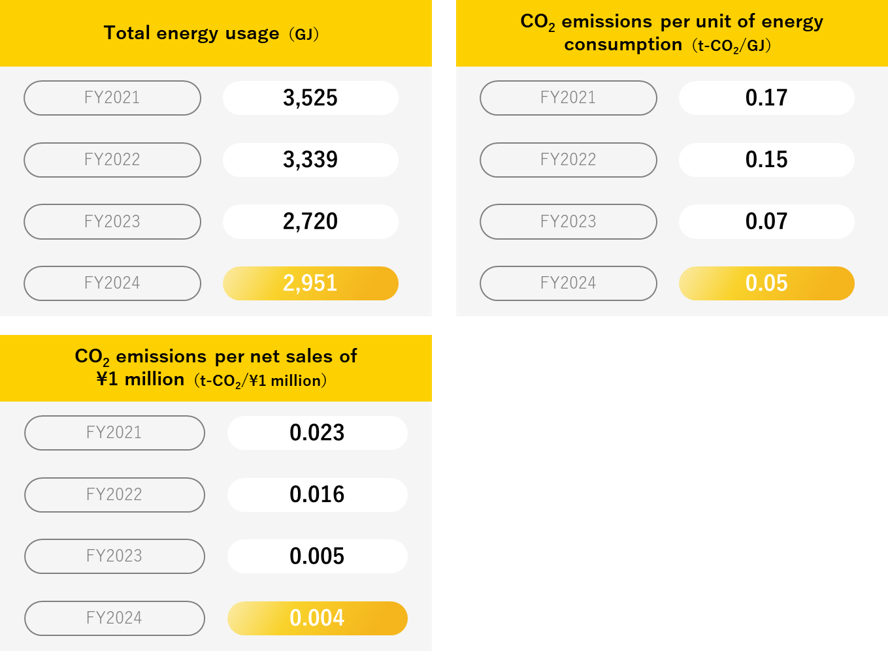
Metrics and Targets
Targets Used to Manage Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities and Results Versus Targets
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Target
Net Zero Target
●Target for electricity from renewable energy sources
The Company has set a target of switching 50% of its electricity consumption at business sites (Head Office, branch and sales offices) to electricity generated from renewable energy sources by FY2030. We are working to transition to carbon-free energy.
●Details on plans for emission reduction activities
The Company is conducting CO2 emissions reduction activities at its business sites, such as upgrading to high-efficiency air conditioning systems, adjusting air conditioning temperature settings to support business-casual attire associated with the Cool Biz and Warm Biz campaigns, and curtailing energy consumption by improving operating efficiency.
●Establishing ways to facilitate emissions reduction activities
Greenhouse gas emissions from the Company’s business activities are attributable to electricity and gas used at business sites. For this reason, we will switch electricity used at business sites to renewable energy and set aside the funds necessary to purchase J-Credits, Green Energy Certificates and Non-Fossil Certificates, as well as engage in steady and continuous activities to achieve carbon neutrality.
●Products and services that can help to reduce third-party emissions (Information Infrastructure Business, Application Service Business, Medical System Business)
In the security field, the introduction of the Group’s offered cloud-based security will eliminate the need for third parties to own and administer server devices and facilities, thereby reducing their electricity consumption and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. In the CRM field, similar benefits can be expected from the introduction of the Company’s cloud-based CRM system. Furthermore, by introducing the Group’s cloud services, third parties in the healthcare field can significantly improve their operational efficiency by utilizing a variety of services. These services include medical imaging management, medical institution support, and AI-powered diagnostic assistance. Reduced operating hours as a result of streamlined operations will result in lower energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from the use of facilities.
The Group strives to make the amount of its contribution transparent by considering how it can assist third parties, including customers, in reducing their greenhouse gas emissions through the use of the aforementioned products and services. The Group is working to increase its business opportunities through these efforts.
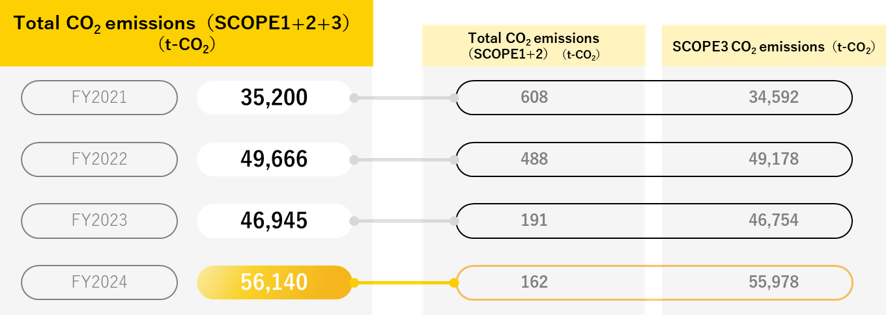
*2 Scope 2 emissions are calculated based on office activities.
*3 For Scope 3 accounting methodologies, the Company has referred to the Basic Guidelines on Accounting for Greenhouse Gas Emissions Throughout the Supply Chain.
*4 Some data items for which data collection is difficult are estimated based on prior performance and other criteria. For this reason, future calculations may be revised, including changes to previously aggregated results.
*5 Currently, data items for which a reasonable computation method cannot be defined are excluded from calculations.
*6 The Company will continually review how to appropriately manage and disclose emissions in each category, taking into account factors such as international discussions.